Задача производительности С++: целое число с преобразованием std::string
Может ли кто-нибудь превзойти производительность моего целого кода std::string, связанного ниже?
Есть несколько вопросов, которые объясняют, как преобразовать целое число в std::string в С++, например этот, но ни одно из предлагаемых решений не является эффективным.
Вот код, готовый для компиляции, для некоторых распространенных методов:
В отличие от популярного мнения, boost::lexical_cast имеет свою собственную реализацию (белая бумага) и не использует операторы stringstream и числовые вставки. Мне бы очень хотелось сравнить его производительность, потому что этот другой вопрос предполагает, что это жалкое.
И мой собственный вклад, который является конкурентоспособным на настольных компьютерах, и демонстрирует подход, который работает на полной скорости и на встроенных системах, в отличие от алгоритмов, зависящих от целочисленного modulo:
Если вы хотите использовать этот код, я сделаю его доступным по упрощенной лицензии BSD (разрешено коммерческое использование, требуется атрибуция). Просто спросите.
Наконец, функция ltoa является нестандартной, но широко доступной.
В скором времени я опубликую свои измерения производительности.
Правила для алгоритмов
- Предоставить код для преобразования по меньшей мере 32-разрядных целых чисел без знака в десятичную.
- Вывести вывод как
std::string.
- Нет трюков, которые несовместимы с потоками и сигналами (например, статические буферы).
- Вы можете принять набор символов ASCII.
- Обязательно проверьте свой код на
INT_MIN на двухкомпонентной машине, где абсолютное значение не представимо.
- В идеале вывод должен быть символьно-символьным, идентичным канонической версии С++, используя
stringstream, http://ideone.com/jh3Sa, но ничего это понятно, так как правильное число тоже нормально.
- NEW. Хотя вы можете использовать любые параметры компилятора и оптимизатора (кроме полностью отключенных), которые вы хотите для сравнения, код также должен компилировать и давать правильные результаты, по крайней мере, на VС++ 2010 и g++.
Обсуждение в режиме ожидания
Помимо улучшенных алгоритмов, я также хотел бы получить некоторые тесты на нескольких разных платформах и компиляторах (позвольте использовать пропускную способность MB/s в качестве нашей стандартной единицы измерения). Я считаю, что код для моего алгоритма (я знаю, что тест sprintf принимает некоторые ярлыки - теперь исправлен) - это четко определенное поведение по стандарту, по крайней мере, по предположению ASCII, но если вы видите поведение undefined или входы, для которых выход недействителен, укажите это.
Выводы:
Различные алгоритмы выполняются для g++ и VC2010, вероятно, из-за разных реализаций std::string для каждого. VC2010 явно улучшает работу с NRVO, избавляясь от возвращаемого значения, помогая только на gcc.
Был найден код, который превосходит sprintf на порядок. ostringstream отстает в 50 и более раз.
Победителем вызова является user434507, который производит код, который работает на 350% от моей собственной скорости на gcc. Другие записи закрыты из-за прихотей сообщества SO.
Текущие (финальные?) чемпионы скорости:
Ответы
Ответ 1
#include <string>
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
std::string& itostr(int n, std::string& s)
{
if(n==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[0];
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
std::string& itostr(unsigned val, std::string& s)
{
if(val==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[size-1];
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
Это взорвется на системах, которые запрещают неприглаженные обращения к памяти (в этом случае первое невыложенное присвоение через *(short*) приведет к segfault), но должно работать очень хорошо в противном случае.
Одна важная вещь - минимизировать использование std::string. (Иронично, я знаю.) В Visual Studio, например, большинство вызовов методов std::string не включены, даже если вы укажете /Ob 2 в параметрах компилятора. Таким образом, даже что-то столь же тривиальное, как вызов std::string::clear(), который вы можете ожидать очень быстро, может принимать 100 тактовых импульсов при связывании CRT в качестве статической библиотеки и до 300 тактовых сигналов при связывании в виде DLL.
По той же причине возвращение по ссылке лучше, потому что оно позволяет избежать назначения, конструктора и деструктора.
Ответ 2
А, потрясающий вызов, кстати... Мне было очень весело с этим.
У меня есть два алгоритма для отправки (код внизу, если вам хочется пропустить его). В моих сравнениях я требую, чтобы функция возвращала строку и могла обрабатывать int и unsigned int. Сравнение вещей, которые не строят строку для тех, которые действительно не имеют смысла.
Первая - это забавная реализация, которая не использует никаких предварительно вычисленных таблиц поиска или явного деления/по модулю. Этот конкурент конкурирует с другими с gcc и со всеми, кроме Timo, на msvc (по уважительной причине, которую я объясняю ниже). Второй алгоритм - мое фактическое представление для максимальной производительности. В моих тестах он превосходит всех остальных как на gcc, так и на msvc.
Я думаю, я знаю, почему некоторые из результатов на MSVC очень хороши. std::string имеет два соответствующих конструктора
std::string(char* str, size_t n)
и
std::string(ForwardIterator b, ForwardIterator e)
gcc делает то же самое для обоих из них... то есть использует второй для реализации первого. Первый конструктор может быть реализован значительно более эффективно, чем это, и MSVC делает это. Преимуществом этого является то, что в некоторых случаях (например, мой быстрый код и код Timo) конструктор строк может быть встроен. Фактически, просто переключение между этими конструкторами в MSVC составляет почти разницу в 2 раза для моего кода.
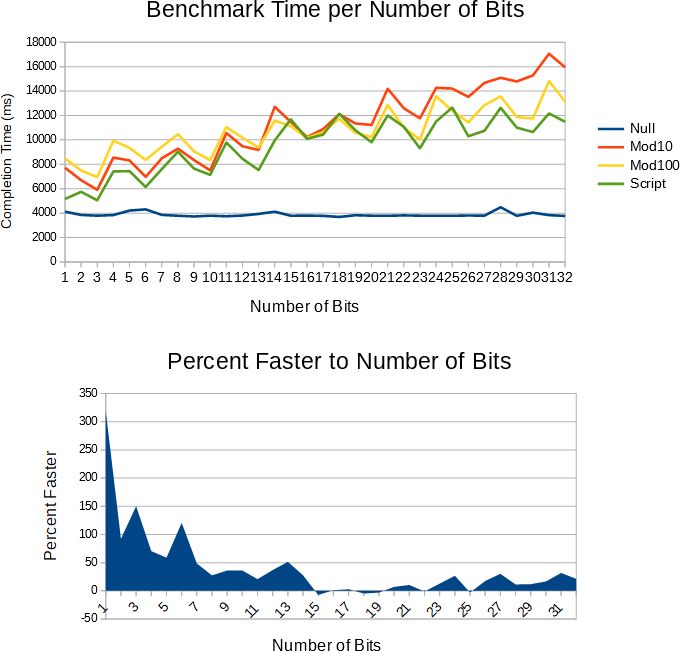
Результаты тестирования производительности:
Источники кода:
- Voigt
- Timo
- ergosys
- user434507
- user-voigt-timo
- hopman-fun
- hopman-fast
gcc 4.4.5-O2 на Ubuntu 10.10 64-бит, Core i5
hopman_fun: 124.688 MB/sec --- 8.020 s
hopman_fast: 137.552 MB/sec --- 7.270 s
voigt: 120.192 MB/sec --- 8.320 s
user_voigt_timo: 97.9432 MB/sec --- 10.210 s
timo: 120.482 MB/sec --- 8.300 s
user: 97.7517 MB/sec --- 10.230 s
ergosys: 101.42 MB/sec --- 9.860 s
MSVC 2010 64-bit/Ox на Windows 7 64-бит, Core i5
hopman_fun: 127 MB/sec --- 7.874 s
hopman_fast: 259 MB/sec --- 3.861 s
voigt: 221.435 MB/sec --- 4.516 s
user_voigt_timo: 195.695 MB/sec --- 5.110 s
timo: 253.165 MB/sec --- 3.950 s
user: 212.63 MB/sec --- 4.703 s
ergosys: 78.0518 MB/sec --- 12.812 s
Вот некоторые результаты и структура тестирования/времени на ideone
http://ideone.com/XZRqp
Обратите внимание, что ideone - это 32-разрядная среда. Оба моих алгоритма страдают от этого, но hopman_fast по крайней мере по-прежнему конкурирует.
Обратите внимание, что для тех, для которых два или около того, которые не строят строку, я добавил следующий шаблон функции:
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T t) {
std::string ret;
itostr(t, ret);
return ret;
}
Теперь для моего кода... сначала веселого:
// hopman_fun
template <typename T>
T reduce2(T v) {
T k = ((v * 410) >> 12) & 0x000F000F000F000Full;
return (((v - k * 10) << 8) + k);
}
template <typename T>
T reduce4(T v) {
T k = ((v * 10486) >> 20) & 0xFF000000FFull;
return reduce2(((v - k * 100) << 16) + (k));
}
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline ull reduce8(ull v) {
ull k = ((v * 3518437209u) >> 45);
return reduce4(((v - k * 10000) << 32) + (k));
}
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
union {
char str[16];
unsigned short u2[8];
unsigned u4[4];
unsigned long long u8[2];
};
unsigned v = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
u8[0] = (ull(v) * 3518437209u) >> 45;
u8[0] = (u8[0] * 28147497672ull);
u8[1] = v - u2[3] * 100000000;
u8[1] = reduce8(u8[1]);
char* f;
if (u2[3]) {
u2[3] = reduce2(u2[3]);
f = str + 6;
} else {
unsigned short* k = u4[2] ? u2 + 4 : u2 + 6;
f = *k ? (char*)k : (char*)(k + 1);
}
if (!*f) f++;
u4[1] |= 0x30303030;
u4[2] |= 0x30303030;
u4[3] |= 0x30303030;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 16) - f);
}
А затем быстрый:
// hopman_fast
struct itostr_helper {
static unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 12) - f);
}
Ответ 3
Контрольные данные для кода, содержащегося в вопросе:
На идеоне (gcc 4.3.4):
Core i7, Windows 7 64-разрядная, 8 ГБ оперативной памяти, Visual С++ 2010 32-разрядная:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- stringstreams: 3,39 МБ/с, 3,67 МБ/с
- sprintf: 16,8 МБ/с, 16,2 МБ/с
- mine: 194 МБ/с, 207 МБ/с (с включенным PGO: 250 МБ/с).
Core i7, Windows 7 64-разрядная, 8 ГБ оперативной памяти, Visual С++ 2010 64-бит:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- stringstreams: 4.42 MB/s, 4.92 MB/s
- sprintf: 21,0 МБ/с, 20,8 МБ/с
- mine: 238 МБ/с, 228 МБ/с
Core i7, Windows 7 64-разрядная, 8 ГБ оперативной памяти, cygwin gcc 4.3.4:
g++ -O3
- stringstreams: 2,19 МБ/с, 2,17 МБ/с
- sprintf: 13,1 МБ/с, 13,4 МБ/с
- mine: 30,0 МБ/с, 30,2 МБ/с
edit: я собирался добавить свой собственный ответ, но вопрос был закрыт, поэтому я добавляю его здесь.:) Я написал свой собственный алгоритм и сумел получить достойное улучшение по сравнению с кодом Ben, хотя я тестировал его только в MSVC 2010. Я также стал эталоном для всех представлений, представленных до сих пор, используя ту же настройку тестирования, что и в оригинале Ben код. - Тимо
Intel Q9450, Win XP 32bit, MSVC 2010
cl /O2 /EHsc
- stringstream: 2.87 МБ/с
- sprintf: 16.1 МБ/с
- Бен: 202 МБ/с
- Ben (неподписанный буфер): 82.0 МБ/с
- ergosys (обновленная версия): 64,2 МБ/с
- user434507: 172 МБ/с
- Timo: 241 МБ/с
-
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
static const int BUFFER_SIZE = 11;
std::string itostr(int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = &buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
if(val>=0) {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
} else {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*val],2);
if(val<=-10)
it--;
*it = '-';
}
return std::string(it,&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-it);
}
std::string itostr(unsigned int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = (char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
return std::string((char*)it,(char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-(char*)it);
}
Ответ 4
Хотя информация, которую мы получаем здесь для алгоритмов, довольно хороша, я думаю, что вопрос "сломан", и я объясню, почему я так думаю:
В вопросе возникает вопрос о выполнении преобразования int → std::string, и это может представлять интерес при сравнении общедоступного метода, такого как различные реализации потокового потока или boost:: lexical_cast. Однако это не имеет смысла, когда вы запрашиваете новый код, специализированный алгоритм, для этого. Причина в том, что int2string всегда будет включать выделение кучи из std::string, и если мы пытаемся выжать последний из нашего алгоритма преобразования, я не думаю, что имеет смысл смешивать эти измерения с выделениями кучи, выполняемыми std::string, Если я хочу выполнить преобразование, я всегда буду использовать буфер фиксированного размера и, конечно же, никогда не выделяю ничего в куче!
Подводя итог, я думаю, что тайминги должны быть разделены:
- Первое, самое быстрое (int → fixed buffer) преобразование.
- Во-вторых, время копирования (фиксированный буфер → std::string).
- В-третьих, проверка того, как распределение std::string может непосредственно использоваться в качестве буфера, чтобы сохранить копирование.
Эти аспекты не должны смешиваться в один момент времени, ИМХО.
Ответ 5
Я не могу тестировать под VS, но это, кажется, быстрее, чем ваш код для g++, около 10%. Возможно, он был настроен,
выбранные значения решений - догадки. int только, извините.
typedef unsigned buf_t;
static buf_t * reduce(unsigned val, buf_t * stp) {
unsigned above = val / 10000;
if (above != 0) {
stp = reduce(above, stp);
val -= above * 10000;
}
buf_t digit = val / 1000;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 1000;
digit = val / 100;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 100;
digit = val / 10;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 10;
*stp++ = val + '0';
return stp;
}
std::string itostr(int input) {
buf_t buf[16];
if(input == INT_MIN) {
char buf2[16];
std::sprintf(buf2, "%d", input);
return std::string(buf2);
}
// handle negative
unsigned val = input;
if(input < 0)
val = -input;
buf[0] = '0';
buf_t* endp = reduce(val, buf+1);
*endp = 127;
buf_t * stp = buf+1;
while (*stp == '0')
stp++;
if (stp == endp)
stp--;
if (input < 0) {
stp--;
*stp = '-';
}
return std::string(stp, endp);
}
Ответ 6
обновил мой ответ... modp_ufast...
Integer To String Test (Type 1)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 1.1633sec Rate:206308473.0686nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 24.3629sec Rate: 9851045.8556nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.2389sec Rate: 45810870.7171nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.3126sec Rate: 72450283.7492nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.0828sec Rate: 77852152.8820nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.7349sec Rate: 50687912.9889nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.1689sec Rate: 46431985.1142nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.6169sec Rate: 51982554.6497nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test(Type 2)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 0.5072sec Rate:473162716.4618nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 22.3483sec Rate: 10739062.9383nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 4.2471sec Rate: 56509024.3035nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.1683sec Rate:110683636.7123nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7133sec Rate: 88454602.1423nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.8030sec Rate: 85623453.3872nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 3.4019sec Rate: 70549286.7776nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7849sec Rate: 86178023.8743nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test (type 3)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 1.6482sec Rate:145610315.7819nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 20.7064sec Rate: 11590618.6109nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.3036sec Rate: 55767734.3570nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 2.9297sec Rate: 81919227.9275nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 3.0278sec Rate: 79266003.8158nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.0631sec Rate: 59068204.3266nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.5616sec Rate: 52613393.0285nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.1248sec Rate: 58184194.4569nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
int ufast_utoa10(unsigned int value, char* str)
{
#define JOIN(N) N "0", N "1", N "2", N "3", N "4", N "5", N "6", N "7", N "8", N "9"
#define JOIN2(N) JOIN(N "0"), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN3(N) JOIN2(N "0"), JOIN2(N "1"), JOIN2(N "2"), JOIN2(N "3"), JOIN2(N "4"), \
JOIN2(N "5"), JOIN2(N "6"), JOIN2(N "7"), JOIN2(N "8"), JOIN2(N "9")
#define JOIN4 JOIN3("0"), JOIN3("1"), JOIN3("2"), JOIN3("3"), JOIN3("4"), \
JOIN3("5"), JOIN3("6"), JOIN3("7"), JOIN3("8"), JOIN3("9")
#define JOIN5(N) JOIN(N), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN6 JOIN5(), JOIN5("1"), JOIN5("2"), JOIN5("3"), JOIN5("4"), \
JOIN5("5"), JOIN5("6"), JOIN5("7"), JOIN5("8"), JOIN5("9")
#define F(N) ((N) >= 100 ? 3 : (N) >= 10 ? 2 : 1)
#define F10(N) F(N),F(N+1),F(N+2),F(N+3),F(N+4),F(N+5),F(N+6),F(N+7),F(N+8),F(N+9)
#define F100(N) F10(N),F10(N+10),F10(N+20),F10(N+30),F10(N+40),\
F10(N+50),F10(N+60),F10(N+70),F10(N+80),F10(N+90)
static const short offsets[] = { F100(0), F100(100), F100(200), F100(300), F100(400),
F100(500), F100(600), F100(700), F100(800), F100(900)};
static const char table1[][4] = { JOIN("") };
static const char table2[][4] = { JOIN2("") };
static const char table3[][4] = { JOIN3("") };
static const char table4[][5] = { JOIN4 };
static const char table5[][4] = { JOIN6 };
#undef JOIN
#undef JOIN2
#undef JOIN3
#undef JOIN4
char *wstr;
int remains[2];
unsigned int v2;
if (value >= 100000000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[1] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
}
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[1]];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
else if (value >= 10000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return 8;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
}
else {
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
str += 4;
*str = 0;
return 4;
} else if (value >= 100) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table3[value];
return 3;
} else if (value >= 10) {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table2[value];
str += 2;
*str = 0;
return 2;
} else {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table1[value];
return 1;
}
}
}
int ufast_itoa10(int value, char* str) {
if (value < 0) { *(str++) = '-';
return ufast_utoa10(-value, str) + 1;
}
else return ufast_utoa10(value, str);
}
void ufast_test() {
print_mode("[modp_ufast]");
std::string s;
s.reserve(32);
std::size_t total_length = 0;
strtk::util::timer t;
t.start();
char buf[128];
int len;
for (int i = (-max_i2s / 2); i < (max_i2s / 2); ++i)
{
#ifdef enable_test_type01
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(((i & 1) ? i : -i), const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type02
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(max_i2s + i, const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type03
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(randval[(max_i2s + i) & 1023], const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
}
t.stop();
printf("Numbers:%10lu\tTotal:%12lu\tTime:%8.4fsec\tRate:%14.4fnums/sec\n",
static_cast<unsigned long>(3 * max_i2s),
static_cast<unsigned long>(total_length),
t.time(),
(3.0 * max_i2s) / t.time());
}
Ответ 7
Вот моя маленькая попытка этой забавной головоломки.
Вместо использования поисковых таблиц мне хотелось, чтобы компилятор все понял. В этом случае, в частности, если вы читаете "Взгляд хакеров", вы видите, как работают деление и модуляция, что позволяет очень оптимизировать это с помощью инструкций SSE/AVX.
Тест производительности
Что касается скорости, мой тест здесь говорит мне в 1,5 раза быстрее, чем работа Тимо (на моем Intel Haswell он работает примерно на 1 ГБ/с).
Что вы можете считать читом
Что касается чита не-make-a-std-string, который я использую, я, конечно же, принял это во внимание и для моего теста Timo.
Я использую внутреннее: BSR. Если вам нравится, вы можете также использовать таблицы DeBruijn вместо этого - это одна из вещей, о которых я много писал в своем "быстром 2log" сообщении. Конечно, у этого есть штраф за производительность (* хорошо... если вы делаете много операций itoa, вы действительно можете сделать более быстрый BSR, но я думаю, что это несправедливо...).
Способ работы
Первое, что нужно сделать, это выяснить, сколько памяти нам нужно. Это в основном 10log, который может быть реализован несколькими интеллектуальными способами. Подробнее см. Часто цитируемый "" Бит Twiddling Hacks".
Следующее, что нужно сделать, это выполнить числовой вывод. Я использую рекурсию шаблона для этого, поэтому компилятор это выяснит.
Я использую 'modulo' и 'div' рядом друг с другом. Если вы прочитаете Hacker Delight, вы заметите, что эти два тесно связаны друг с другом, поэтому, если у вас есть один ответ, у вас, вероятно, есть и другой. Я понял, что компилятор может выяснить детали...: -)
Код
Получение числа цифр с использованием (измененного) журнала10:
struct logarithm
{
static inline int log2(unsigned int value)
{
unsigned long index;
if (!_BitScanReverse(&index, value))
{
return 0;
}
// add 1 if x is NOT a power of 2 (to do the ceil)
return index + (value&(value - 1) ? 1 : 0);
}
static inline int numberDigits(unsigned int v)
{
static unsigned int const PowersOf10[] =
{ 0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000 };
int t = (logarithm::log2(v) + 1) * 1233 >> 12; // (use a lg2 method from above)
return 1 + t - (v < PowersOf10[t]);
}
};
Получение строки:
template <int count>
struct WriteHelper
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
unsigned int div = value / 10;
unsigned int rem = value % 10;
buf[count - 1] = rem + '0';
WriteHelper<count - 1>::WriteChar(buf, div);
}
};
template <>
struct WriteHelper<1>
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
buf[0] = '0' + value;
}
};
// Boring code that converts a length into a switch.
// TODO: Test if recursion with an 'if' is faster.
static inline void WriteNumber(char* data, int len, unsigned int val)
{
switch (len) {
case 1:
WriteHelper<1>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 2:
WriteHelper<2>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 3:
WriteHelper<3>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 4:
WriteHelper<4>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 5:
WriteHelper<5>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 6:
WriteHelper<6>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 7:
WriteHelper<7>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 8:
WriteHelper<8>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 9:
WriteHelper<9>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 10:
WriteHelper<10>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
}
}
// The main method you want to call...
static int Write(char* data, int val)
{
int len;
if (val >= 0)
{
len = logarithm::numberDigits(val);
WriteNumber(data, len, unsigned int(val));
return len;
}
else
{
unsigned int v(-val);
len = logarithm::numberDigits(v);
WriteNumber(data+1, len, v);
data[0] = '-';
return len + 1;
}
}
Ответ 8
У меня было это сидение некоторое время, и, наконец, он собрался, чтобы опубликовать его.
Еще несколько методов по сравнению с двойным словом в момент hopman_fast. Результаты для оптимизированного с использованием коротких строк std::string GCC, так как в противном случае разницы в производительности будут затенены накладными расходами кода управления строкой копирования на запись. Пропускная способность измеряется так же, как и в других разделах этой темы, количество циклов для исходных сериализационных частей кода до копирования выходного буфера в строку.
HOPMAN_FAST - performance reference
TM_CPP, TM_VEC - scalar and vector versions of Terje Mathisen algorithm
WM_VEC - intrinsics implementation of Wojciech Mula vector algorithm
AK_BW - word-at-a-time routine with a jump table that fills a buffer in reverse
AK_FW - forward-stepping word-at-a-time routine with a jump table in assembly
AK_UNROLLED - generic word-at-a-time routine that uses an unrolled loop
![Throughput]()
![Raw cost]()
Коммутаторы времени компиляции:
-DVSTRING - позволяет использовать SSO-строки для более старых настроек GCC
-DBSR1 - позволяет быстро log10
-DRDTSC - включает счетчики циклов
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <limits>
#include <ctime>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/* Uncomment to run */
// #define HOPMAN_FAST
// #define TM_CPP
// #define TM_VEC
// #define WM_VEC
// #define AK_UNROLLED
// #define AK_BW
// #define AK_FW
using namespace std;
#ifdef VSTRING
#include <ext/vstring.h>
typedef __gnu_cxx::__vstring string_type;
#else
typedef string string_type;
#endif
namespace detail {
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define ALIGN(N) __attribute__ ((aligned(N)))
#define PACK __attribute__ ((packed))
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned u) {
struct {
uint32_t count;
uint32_t max;
} static digits[32] ALIGN(64) = {
{ 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 },
{ 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 },
{ 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 },
{ 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 },
{ 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 },
{ 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 },
{ 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 },
{ 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 },
{ 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 },
{ 10, UINT_MAX }, { 10, UINT_MAX }
};
#if (defined(i386) || defined(__x86_64__)) && (defined(BSR1) || defined(BSR2))
size_t l = u;
#if defined(BSR1)
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"bsrl %k0, %k0 \n\t"
"shlq $32, %q1 \n\t"
"movq %c2(,%0,8), %0\n\t"
"cmpq %0, %q1 \n\t"
"seta %b1 \n\t"
"addl %1, %k0 \n\t"
: "+r" (l), "+r"(u)
: "i"(digits)
: "cc"
);
return l;
#else
__asm__ __volatile__ ( "bsr %0, %0;" : "+r" (l) );
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
#else
size_t l = (u != 0) ? 31 - __builtin_clz(u) : 0;
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
}
#else
inline unsigned msb_u32(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned bval[] = { 0,1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,4,4 };
unsigned base = 0;
if (x & (unsigned) 0xFFFF0000) { base += 32/2; x >>= 32/2; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x0000FF00) { base += 32/4; x >>= 32/4; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x000000F0) { base += 32/8; x >>= 32/8; }
return base + bval[x];
}
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned powertable[] = {
0,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000,10000000,100000000, 1000000000 };
size_t lg_ten = msb_u32(x) * 1233 >> 12;
size_t adjust = (x >= powertable[lg_ten]);
return lg_ten + adjust;
}
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
struct CharBuffer {
class reverse_iterator : public iterator<random_access_iterator_tag, char> {
char* m_p;
public:
reverse_iterator(char* p) : m_p(p - 1) {}
reverse_iterator operator++() { return --m_p; }
reverse_iterator operator++(int) { return m_p--; }
char operator*() const { return *m_p; }
bool operator==( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p == it.m_p; }
bool operator!=( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p != it.m_p; }
difference_type operator-( reverse_iterator it) const { return it.m_p - m_p; }
};
};
union PairTable {
char c[2];
unsigned short u;
} PACK table[100] ALIGN(1024) = {
{{'0','0'}},{{'0','1'}},{{'0','2'}},{{'0','3'}},{{'0','4'}},{{'0','5'}},{{'0','6'}},{{'0','7'}},{{'0','8'}},{{'0','9'}},
{{'1','0'}},{{'1','1'}},{{'1','2'}},{{'1','3'}},{{'1','4'}},{{'1','5'}},{{'1','6'}},{{'1','7'}},{{'1','8'}},{{'1','9'}},
{{'2','0'}},{{'2','1'}},{{'2','2'}},{{'2','3'}},{{'2','4'}},{{'2','5'}},{{'2','6'}},{{'2','7'}},{{'2','8'}},{{'2','9'}},
{{'3','0'}},{{'3','1'}},{{'3','2'}},{{'3','3'}},{{'3','4'}},{{'3','5'}},{{'3','6'}},{{'3','7'}},{{'3','8'}},{{'3','9'}},
{{'4','0'}},{{'4','1'}},{{'4','2'}},{{'4','3'}},{{'4','4'}},{{'4','5'}},{{'4','6'}},{{'4','7'}},{{'4','8'}},{{'4','9'}},
{{'5','0'}},{{'5','1'}},{{'5','2'}},{{'5','3'}},{{'5','4'}},{{'5','5'}},{{'5','6'}},{{'5','7'}},{{'5','8'}},{{'5','9'}},
{{'6','0'}},{{'6','1'}},{{'6','2'}},{{'6','3'}},{{'6','4'}},{{'6','5'}},{{'6','6'}},{{'6','7'}},{{'6','8'}},{{'6','9'}},
{{'7','0'}},{{'7','1'}},{{'7','2'}},{{'7','3'}},{{'7','4'}},{{'7','5'}},{{'7','6'}},{{'7','7'}},{{'7','8'}},{{'7','9'}},
{{'8','0'}},{{'8','1'}},{{'8','2'}},{{'8','3'}},{{'8','4'}},{{'8','5'}},{{'8','6'}},{{'8','7'}},{{'8','8'}},{{'8','9'}},
{{'9','0'}},{{'9','1'}},{{'9','2'}},{{'9','3'}},{{'9','4'}},{{'9','5'}},{{'9','6'}},{{'9','7'}},{{'9','8'}},{{'9','9'}}
};
} // namespace detail
struct progress_timer {
clock_t c;
progress_timer() : c(clock()) {}
int elapsed() { return clock() - c; }
~progress_timer() {
clock_t d = clock() - c;
cout << d / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "."
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 1000 / 100)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 100 / 10)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 10)
<< " s" << endl;
}
};
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
namespace hopman_fast {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
struct itostr_helper {
static ALIGN(1024) unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
string_type itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
str += 12;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(f, str);
}
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
namespace ak {
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
namespace unrolled {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static const size_t MaxValueSize = 16;
static inline char* generate(int value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value < 0 ? unsigned(~value) + 1 : value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
*(b.pc -= (u >= 10)) = '-';
return b.pc + (value >= 0);
}
static inline char* generate(unsigned value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
return b.pc + (u < 10);
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(value_type v) {
char buf[MaxValueSize];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char* p = generate(v, buf);
char* e = buf + MaxValueSize;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(p, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
namespace bw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint64_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
u_type u = v;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 8) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 8: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 6) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 6: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 4) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 4: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 2) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)buffer = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 7) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 7: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 5) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 5: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 3) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 3: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 1) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 1: *buffer = v + 0x30;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + neg;
generate(val, len, e);
e += len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
namespace fw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint32_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
uint16_t w;
uint32_t u;
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"jmp %*T%=(,%3,8) \n\t"
"T%=: .quad L0%= \n\t"
" .quad L1%= \n\t"
" .quad L2%= \n\t"
" .quad L3%= \n\t"
" .quad L4%= \n\t"
" .quad L5%= \n\t"
" .quad L6%= \n\t"
" .quad L7%= \n\t"
" .quad L8%= \n\t"
" .quad L9%= \n\t"
" .quad L10%= \n\t"
"L10%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1441151881, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $57, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L8%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1125899907, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $50, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -8(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L6%=: \n\t"
" imulq $429497, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $32, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -6(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L4%=: \n\t"
" imull $167773, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $24, %1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -4(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L2%=: \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q0,2), %w2 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -2(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L0%=: jmp 1f \n\t"
"L9%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1801439851, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $54, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L7%=: \n\t"
" imulq $43980466, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $42, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -7(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L5%=: \n\t"
" imulq $268436, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $28, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -5(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L3%=: \n\t"
" imull $6554, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $15, %1 \n\t"
" andb $254, %b1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1), %w2 \n\t"
" leal (%1,%1,4), %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -3(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L1%=: \n\t"
" addl $48, %0 \n\t"
" movb %b0, -1(%4,%3) \n\t"
"1: \n\t"
: "+r"(v), "=&q"(u), "=&r"(w)
: "r"(len), "r"(buffer), "i"(detail::table)
: "memory", "cc"
);
#else
u_type u;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1441151881ULL) >> 57; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000000;
case 8: u = (v * 1125899907ULL) >> 50; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 8) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000000;
case 6: u = (v * 429497ULL) >> 32; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 6) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000;
case 4: u = (v * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 4) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 2) = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1801439851ULL) >> 54; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000000;
case 7: u = (v * 43980466ULL) >> 42; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 7) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000;
case 5: u = (v * 268436ULL) >> 28; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 5) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000;
case 3: u = (v * 6554) >> 16; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 3) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10;
case 1: *(buffer + len - 1) = v + 0x30;
}
#endif
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
if (neg) buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + len + neg;
generate(val, len, buf + neg);
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
} // ak
namespace wm {
#ifdef WM_VEC
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned v, char* buf) {
static struct {
unsigned short mul_10[8];
unsigned short div_const[8];
unsigned short shl_const[8];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits =
{
{ // mul_10
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10
},
{ // div_const
8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000, 8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000
},
{ // shl_const
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15),
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15)
},
{ // to_ascii
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0'
}
};
unsigned x, y, l;
x = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37;
y = v;
l = 0;
if (x) {
unsigned div = 0xd1b71759;
unsigned mul = 55536;
__m128i z, m, a, o;
y -= 100 * x;
z = _mm_cvtsi32_si128(x);
m = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
o = _mm_mul_epu32( z, _mm_cvtsi32_si128(div));
z = _mm_add_epi32( z, _mm_mul_epu32( _mm_cvtsi32_si128(mul), _mm_srli_epi64( o, 45) ) );
z = _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_unpacklo_epi16(z, z), 5 ), 2 );
a = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
z = _mm_mulhi_epu16( _mm_mulhi_epu16( z, *(__m128i*)bits.div_const ), *(__m128i*)bits.shl_const );
z = _mm_sub_epi16( z, _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi16( m, z ), 16 ) );
z = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_packus_epi16( z, _mm_xor_si128(o, o) ), a );
x = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( a, z ) ) );
l = 8 - x;
uint64_t q = _mm_cvtsi128_si64(z) >> (x * 8);
*(uint64_t*)buf = q;
buf += l;
x = 1;
}
v = (y * 6554) >> 16;
l += 1 + (x | (v != 0));
*(unsigned short*)buf = 0x30 + ((l > 1) ? ((0x30 + y - v * 10) << 8) + v : y);
return l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
buf[0] = '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf + neg);
char* e = buf + len + neg;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
inline string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
inline string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#endif
} // wm
namespace tmn {
#ifdef TM_CPP
namespace cpp {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, char* buffer) {
unsigned const f1_10000 = (1 << 28) / 10000;
unsigned tmplo, tmphi;
unsigned lo = v % 100000;
unsigned hi = v / 100000;
tmplo = lo * (f1_10000 + 1) - (lo >> 2);
tmphi = hi * (f1_10000 + 1) - (hi >> 2);
unsigned mask = 0x0fffffff;
unsigned shift = 28;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
buffer[i + 0] = '0' + (char)(tmphi >> shift);
buffer[i + 5] = '0' + (char)(tmplo >> shift);
tmphi = (tmphi & mask) * 5;
tmplo = (tmplo & mask) * 5;
mask >>= 1;
shift--;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char buf[16];
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
char* e = buf + 11;
generate(val, buf + 1);
buf[10 - len] = '-';
len += neg;
char* b = e - len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(b, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned val, char* buffer) {
static struct {
unsigned char mul_10[16];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
unsigned char gather[16];
unsigned char shift[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits = {
{ 10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0 },
{ '0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0' },
{ 3,5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 }
};
unsigned u = val / 1000000;
unsigned l = val - u * 1000000;
__m128i x, h, f, m, n;
n = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
x = _mm_set_epi64x( l, u );
h = _mm_mul_epu32( x, _mm_set1_epi32(4294968) );
x = _mm_sub_epi64( x, _mm_srli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi32( h, _mm_set1_epi32(1000) ), 32 ) );
f = _mm_set1_epi32((1 << 28) / 1000 + 1);
m = _mm_srli_epi32( _mm_cmpeq_epi32(m, m), 4 );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_blend_epi16( x, h, 204 ), 177 );
f = _mm_sub_epi32( _mm_mullo_epi32(f, x), _mm_srli_epi32(x, 2) );
h = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
x = _mm_srli_epi32(f, 28);
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 8) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 16) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 24) );
x = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_shuffle_epi8(x, *(__m128i*)bits.gather), h );
l = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( h, x ) ) | (1 << 9) );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi8( x, _mm_add_epi8(*(__m128i*)bits.shift, _mm_set1_epi8(l) ) );
_mm_store_si128( (__m128i*)buffer, x );
return 10 - l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char arena[32];
char* buf = (char*)((uintptr_t)(arena + 16) & ~(uintptr_t)0xf);
*(buf - 1)= '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf) + neg;
buf -= neg;
char* end = buf + len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, end);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
}
bool fail(string in, string_type out) {
cout << "failure: " << in << " => " << out << endl;
return false;
}
#define TEST(x, n) \
stringstream ss; \
string_type s = n::itostr(x); \
ss << (long long)x; \
if (::strcmp(ss.str().c_str(), s.c_str())) { \
passed = fail(ss.str(), s); \
break; \
}
#define test(x) { \
passed = true; \
if (0 && passed) { \
char c = CHAR_MIN; \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != CHAR_MAX); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed char!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (0 && passed) { \
short c = numeric_limits<short>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != numeric_limits<short>::max()); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed short!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
int c = numeric_limits<int>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c += 100000) < numeric_limits<int>::max() - 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed int!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
unsigned c = numeric_limits<unsigned>::max(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c -= 100000) > 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed unsigned int!!!" << endl; \
} \
}
#define time(x, N) \
if (passed) { \
static const int64_t limits[] = \
{0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, \
1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000, 10000000000ULL }; \
long passes = 0; \
cout << #x << ": "; \
progress_timer t; \
uint64_t s = 0; \
if (do_time) { \
for (int n = 0; n < N1; n++) { \
int i = 0; \
while (i < N2) { \
int v = ((NM - i) % limits[N]) | (limits[N] / 10); \
int w = x::itostr(v).size() + \
x::itostr(-v).size(); \
i += w * mult; \
passes++; \
} \
s += i / mult; \
} \
} \
k += s; \
cout << N << " digits: " \
<< s / double(t.elapsed()) * CLOCKS_PER_SEC/1000000 << " MB/sec, " << (x::cycles() / passes >> 1) << " clocks per pass "; \
x::reset(); \
}
#define series(n) \
{ if (do_test) test(n); if (do_time) time(n, 1); if (do_time) time(n, 2); \
if (do_time) time(n, 3); if (do_time) time(n, 4); if (do_time) time(n, 5); \
if (do_time) time(n, 6); if (do_time) time(n, 7); if (do_time) time(n, 8); \
if (do_time) time(n, 9); if (do_time) time(n, 10); }
int N1 = 1, N2 = 500000000, NM = INT_MAX;
int mult = 1; // used to stay under timelimit on ideone
unsigned long long k = 0;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
bool do_time = 1, do_test = 1;
bool passed = true;
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
series(hopman_fast)
#endif
#ifdef WM_VEC
series(wm::vec)
#endif
#ifdef TM_CPP
series(tmn::cpp)
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
series(tmn::vec)
#endif
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
series(ak::unrolled)
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
series(ak::bw)
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
series(ak::fw)
#endif
return k;
}
Ответ 9
Я считаю, что создал быстрый алгоритм с целыми целыми строками. Это вариант алгоритма Modulo 100, который примерно на 33% быстрее, и, самое главное, он быстрее для меньших и больших чисел. Он называется алгоритмом Script ItoS. Чтобы прочитать статью, в которой объясняется, как я разработал алгоритм @see https://github.com/kabuki-starship/kabuki-toolkit/wiki/Engineering-a-Faster-Integer-to-String-Algorithm. Вы можете использовать алгоритм, но, пожалуйста, подумайте о том, чтобы внести вклад в VM Kabuki и проверить скрипт; особенно если вас интересуют AMIL-NLP и/или программные сетевые протоколы.
![enter image description here]()
/** Kabuki Toolkit
@version 0.x
@file ~/source/crabs/print_itos.cc
@author Cale McCollough <[email protected]>
@license Copyright (C) 2017-2018 Cale McCollough <[email protected]>;
All right reserved (R). Licensed under the Apache License, Version
2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in
compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License
[here](http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0). Unless
required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
implied. See the License for the specific language governing
permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
#include <stdafx.h>
#include "print_itos.h"
#if MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
#define DEBUG 1
#define PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__);
#define PUTCHAR(c) putchar(c);
#define PRINT_PRINTED\
sprintf_s (buffer, 24, "%u", value); *text_end = 0;\
printf ("\n Printed \"%s\" leaving value:\"%s\":%u",\
begin, buffer, (uint)strlen (buffer));
#define PRINT_BINARY PrintBinary (value);
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE PrintBinaryTable (value);
#else
#define PRINTF(x, ...)
#define PUTCHAR(c)
#define PRINT_PRINTED
#define PRINT_BINARY
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE
#endif
namespace _ {
void PrintLine (char c) {
std::cout << '\n';
for (int i = 80; i > 0; --i)
std::cout << c;
}
char* Print (uint32_t value, char* text, char* text_end) {
// Lookup table for powers of 10.
static const uint32_t k10ToThe[]{
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000,
1000000000, ~(uint32_t)0 };
/** Lookup table of ASCII char pairs for 00, 01, ..., 99.
To convert this algorithm to big-endian, flip the digit pair bytes. */
static const uint16_t kDigits00To99[100] = {
0x3030, 0x3130, 0x3230, 0x3330, 0x3430, 0x3530, 0x3630, 0x3730, 0x3830,
0x3930, 0x3031, 0x3131, 0x3231, 0x3331, 0x3431, 0x3531, 0x3631, 0x3731,
0x3831, 0x3931, 0x3032, 0x3132, 0x3232, 0x3332, 0x3432, 0x3532, 0x3632,
0x3732, 0x3832, 0x3932, 0x3033, 0x3133, 0x3233, 0x3333, 0x3433, 0x3533,
0x3633, 0x3733, 0x3833, 0x3933, 0x3034, 0x3134, 0x3234, 0x3334, 0x3434,
0x3534, 0x3634, 0x3734, 0x3834, 0x3934, 0x3035, 0x3135, 0x3235, 0x3335,
0x3435, 0x3535, 0x3635, 0x3735, 0x3835, 0x3935, 0x3036, 0x3136, 0x3236,
0x3336, 0x3436, 0x3536, 0x3636, 0x3736, 0x3836, 0x3936, 0x3037, 0x3137,
0x3237, 0x3337, 0x3437, 0x3537, 0x3637, 0x3737, 0x3837, 0x3937, 0x3038,
0x3138, 0x3238, 0x3338, 0x3438, 0x3538, 0x3638, 0x3738, 0x3838, 0x3938,
0x3039, 0x3139, 0x3239, 0x3339, 0x3439, 0x3539, 0x3639, 0x3739, 0x3839,
0x3939, };
static const char kMsbShift[] = { 4, 7, 11, 14, 17, 21, 24, 27, 30, };
if (!text) {
return nullptr;
}
if (text >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
uint16_t* text16;
char digit;
uint32_t scalar;
uint16_t digits1and2,
digits3and4,
digits5and6,
digits7and8;
uint32_t comparator;
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
// Write a bunches of xxxxxx to the buffer for debug purposes.
for (int i = 0; i <= 21; ++i) {
*(text + i) = 'x';
}
*(text + 21) = 0;
char* begin = text;
char buffer[256];
#endif
if (value < 10) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[0, 9] length:1 ")
if (text + 1 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '0' + (char)value;
PRINT_PRINTED
return text;
}
if (value < 100) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10, 99] length:2 ")
if (text + 2 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[value];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 2;
}
if (value >> 14) {
if (value >> 27) {
if (value >> 30) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1073741824, 4294967295] length:10")
Print10:
if (text + 10 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)(value / comparator);
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
value -= digits1and2 * comparator;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
text += 2;
goto Print8;
}
else {
comparator = 1000000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 1073741823] length:10")
goto Print10;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[134217727, 999999999] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digit = (char)(value / comparator);
*text++ = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator * digit;
goto Print8;
}
}
else if (value >> 24) {
comparator = k10ToThe[8];
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 134217728] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[16777216, 9999999] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
Print8:
PRINTF ("\n Print8:")
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) =
kDigits00To99[digits7and8];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 8;
}
else if (value >> 20) {
comparator = 10000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000000, 16777215] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1048576, 9999999] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 5) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text = (char)digits7and8 + '0';
return text + 7;
}
else if (value >> 17) {
comparator = 1000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000, 1048575] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[131072, 999999] length:6")
if (text + 6 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
Print6:
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6);
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 6;
}
else { // (value >> 14)
if (value >= 100000) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[65536, 131071] length:6")
goto Print6;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 65535] length:5")
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits5and6 = 10000;
digit = (uint8_t)(value / digits5and6);
value -= digits5and6 * digit;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 5;
}
}
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
if (value >> 10) {
digits5and6 = 10000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits5and6) {
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 16383] length:5")
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 -= digits5and6;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1024, 9999] length:4")
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
else {
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits3and4 = 1000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits3and4) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1000, 1023] length:4")
digits1and2 -= digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2);
*text16-- = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text16 = (((uint16_t)'1') | (((uint16_t)'0') << 8));
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100, 999] length:3")
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits3and4 = 100;
digit = (char)(digits1and2 / digits3and4);
digits1and2 -= digit * digits3and4;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 3;
}
}
} //< namespace _
#undef PRINTF
#undef PRINT_PRINTED
#endif //< MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
автор
Ответ 10
Модификация для решения user434507. Изменено использование символьного массива вместо строки С++. Выполняется немного быстрее. Также переместил чек на 0 ниже кода... поскольку это никогда не случается для моего конкретного случая. Переместите его назад, если это более распространено для вашего случая.
// Int2Str.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "StopWatch.h"
using namespace std;
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
void itostr(int n, char* c) {
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000) {
if(val>=10000000) {
if(val>=1000000000) {
size=10;
}
else if(val>=100000000) {
size=9;
}
else size=8;
}
else {
if(val>=1000000) {
size=7;
}
else if(val>=100000) {
size=6;
}
else size=5;
}
}
else {
if(val>=100) {
if(val>=1000) {
size=4;
}
else size=3;
}
else {
if(val>=10) {
size=2;
}
else if(n==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100) {
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0) {
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void itostr(unsigned val, char* c)
{
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else if (val==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else
size=1;
}
}
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void test() {
bool foundmismatch = false;
char str[16];
char compare[16];
for(int i = -1000000; i < 1000000; i++) {
int random = rand();
itostr(random, str);
itoa(random, compare, 10);
if(strcmp(str, compare) != 0) {
cout << "Mismatch found: " << endl;
cout << "Generated: " << str << endl;
cout << "Reference: " << compare << endl;
foundmismatch = true;
}
}
if(!foundmismatch) {
cout << "No mismatch found!" << endl;
}
cin.get();
}
void benchmark() {
StopWatch stopwatch;
stopwatch.setup("Timer");
stopwatch.reset();
stopwatch.start();
char str[16];
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) {
itostr(i, str);
}
stopwatch.stop();
cin.get();
}
int main( int argc, const char* argv[]) {
benchmark();
}
Ответ 11
Мы используем следующий код (для MSVC):
Templated tBitScanReverse:
#include <intrin.h>
namespace intrin {
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse)
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse64)
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 4), unsigned char>
{
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, mask);
}
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 8), unsigned char>
{
#if !(_M_IA64 || _M_AMD64)
auto res = _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)(mask >> 32));
if (res) {
out_index += 32;
return res;
}
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)mask);
#else
return _BitScanReverse64(out_index, mask);
#endif
}
}
char/wchar_t помощники:
template<typename TChar> inline constexpr TChar ascii_0();
template<> inline constexpr char ascii_0() { return '0'; }
template<> inline constexpr wchar_t ascii_0() { return L'0'; }
template<typename TChar, typename TInt> inline constexpr TChar ascii_DEC(TInt d) { return (TChar)(ascii_0<TChar>() + d); }
Полнота 10 таблиц:
static uint32 uint32_powers10[] = {
1,
10,
100,
1000,
10000,
100000,
1000000,
10000000,
100000000,
1000000000
// 123456789
};
static uint64 uint64_powers10[] = {
1ULL,
10ULL,
100ULL,
1000ULL,
10000ULL,
100000ULL,
1000000ULL,
10000000ULL,
100000000ULL,
1000000000ULL,
10000000000ULL,
100000000000ULL,
1000000000000ULL,
10000000000000ULL,
100000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000ULL,
100000000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000000ULL
// 1234567890123456789
};
template<typename TUint> inline constexpr const TUint * powers10();
template<> inline constexpr const uint32 * powers10() { return uint32_powers10; }
template<> inline constexpr const uint64 * powers10() { return uint64_powers10; }
Фактическая печать:
template<typename TChar, typename TUInt>
__forceinline auto
print_dec(
TUInt u,
TChar * & buffer) -> typename std::enable_if_t<std::is_unsigned<TUInt>::value>
{
if (u < 10) { // 1-digit, including 0
*buffer++ = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
else {
DWORD log2u;
intrin::tBitScanReverse(&log2u, u); // log2u [3,31] (u >= 10)
DWORD log10u = ((log2u + 1) * 77) >> 8; // log10u [1,9] 77/256 = ln(2) / ln(10)
DWORD digits = log10u + (u >= powers10<TUInt>()[log10u]); // digits [2,10]
buffer += digits;
auto p = buffer;
for (--digits; digits; --digits) {
auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10;
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d);
u = x;
}
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
}
Последний цикл можно развернуть:
switch (digits) {
case 10: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 9: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 8: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 7: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 6: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 5: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 4: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 3: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 2: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u); break; }
default: __assume(0);
}
Основная идея - это то же самое, что и раньше: @atlaste: fooobar.com/questions/6636/...
Ответ 12
Просто сталкивался с этим из-за недавней активности; У меня действительно нет времени, чтобы добавить тесты, но я хотел добавить то, что писал в прошлом, когда мне нужно быстрое преобразование целых чисел в строки...
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.h
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.cxx
Здесь используется хитрость: пользователь должен предоставить достаточно большой массив std :: (в своем стеке), и этот код записывает в него строку в обратном направлении, начиная с единиц измерения, а затем возвращает указатель в массив со смещением где результат фактически начинается.
Следовательно, это не выделяет и не перемещает память, но все же требует деления и модуляции для каждой результирующей цифры (что я считаю достаточно быстрым, поскольку это просто код, выполняемый внутри ЦП; доступ к памяти обычно является проблемой imho).
Ответ 13
Почему никто не использует функцию div из stdlib, когда нужны как частное, так и остальное?
Используя исходный код Timo, я получил что-то вроде этого:
if(val >= 0)
{
div_t d2 = div(val,100);
while(d2.quot)
{
COPYPAIR(it,2 * d2.rem);
it-=2;
d2 = div(d2.quot,100);
}
COPYPAIR(it,2*d2.rem);
if(d2.quot<10)
it++;
}
else
{
div_t d2 = div(val,100);
while(d2.quot)
{
COPYPAIR(it,-2 * d2.rem);
it-=2;
d2 = div(d2.quot,100);
}
COPYPAIR(it,-2*d2.rem);
if(d2.quot<=-10)
it--;
*it = '-';
}
Хорошо, для unsigned int, функция div не может использоваться, но без знака может обрабатываться отдельно.
Я определил макрос COPYPAIR следующим образом, чтобы проверить варианты, как скопировать 2 символа из digit_pairs (не нашел очевидного преимущества любого из этих методов):
#define COPYPAIR0(_p,_i) { memcpy((_p), &digit_pairs[(_i)], 2); }
#define COPYPAIR1(_p,_i) { (_p)[0] = digit_pairs[(_i)]; (_p)[1] = digit_pairs[(_i)+1]; }
#define COPYPAIR2(_p,_i) { unsigned short * d = (unsigned short *)(_p); unsigned short * s = (unsigned short *)&digit_pairs[(_i)]; *d = *s; }
#define COPYPAIR COPYPAIR2